1980
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
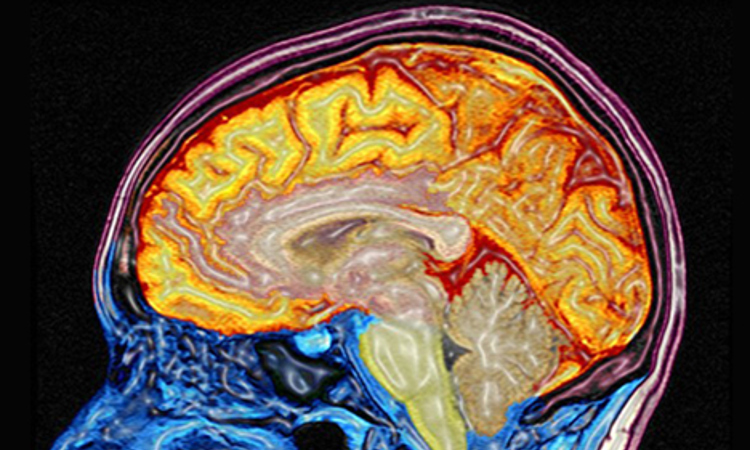
MRI is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to investigate the anatomy and function of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields and radiowaves to form images of the body. The technique is widely used in hospitals for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and for follow-up without exposure to ionizing radiation. During the 1970s a team led by Scottish professor John Mallard built the first full body MRI scanner at the University of Aberdeen. On 28 August 1980 they used this machine to obtain the first clinically useful image of a patient’s internal tissues using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which identified a primary tumour in the patients chest, an abnormal liver, and secondary cancer in his bone.For more information: Visit this article by Professor Mallard.
Image courtesy of Wellcome Library, London